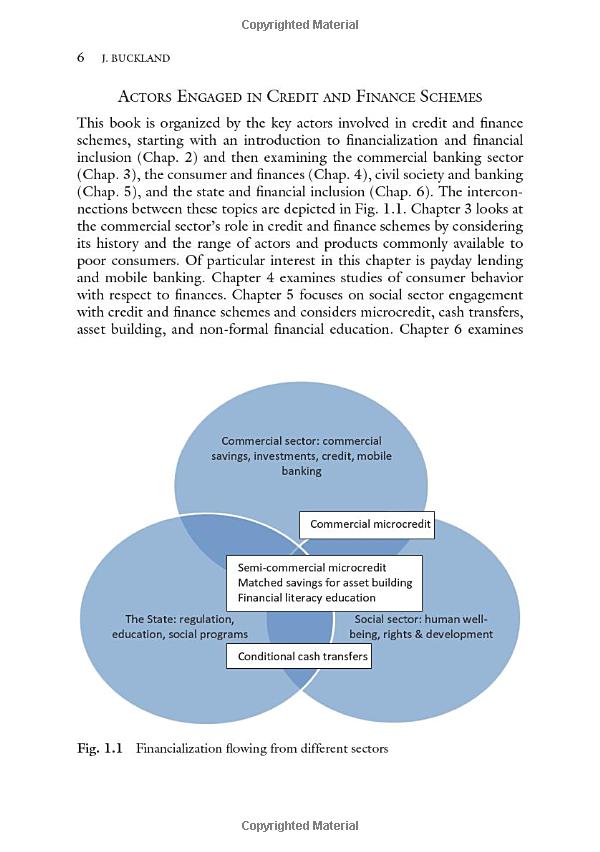
Understanding the US Department of Education Loan Forgiveness Programs: A Comprehensive Guide to Financial Relief
#### US Department of Education Loan ForgivenessThe **US Department of Education Loan Forgiveness** programs are designed to alleviate the burden of student……
#### US Department of Education Loan Forgiveness
The **US Department of Education Loan Forgiveness** programs are designed to alleviate the burden of student loans for eligible borrowers. These programs aim to provide financial relief to individuals who have dedicated their careers to public service, teaching, and other qualifying professions. Understanding the intricacies of these forgiveness options is crucial for borrowers seeking to manage their student debt effectively.
#### What is Loan Forgiveness?
Loan forgiveness refers to the cancellation of a borrower's obligation to repay some or all of their student loans. The US Department of Education offers several forgiveness programs, each with specific eligibility criteria and application processes. These programs can significantly reduce the financial strain on borrowers, especially those working in lower-paying jobs that serve the public good.
#### Types of Loan Forgiveness Programs
There are several types of loan forgiveness programs available through the US Department of Education, including:
1. **Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF)**:
This program is designed for borrowers who work full-time in qualifying public service jobs. After making 120 qualifying monthly payments under a qualifying repayment plan, borrowers may have the remaining balance of their Direct Loans forgiven.
2. **Teacher Loan Forgiveness**:

Teachers who work in low-income schools or subject areas may qualify for forgiveness of up to $17,500 on their Direct Subsidized and Unsubsidized Loans or Stafford Loans after five consecutive years of teaching.
3. **Income-Driven Repayment (IDR) Forgiveness**:
Borrowers enrolled in an IDR plan may have their remaining loan balance forgiven after making payments for 20 or 25 years, depending on the plan.
4. **Perkins Loan Cancellation**:
Certain professions, such as teaching, nursing, and law enforcement, may qualify for cancellation of Perkins Loans after a specified period of service.
#### Eligibility Criteria
To qualify for these forgiveness programs, borrowers must meet specific criteria, which may include:

- Employment in a qualifying field (e.g., public service, teaching)
- Making a certain number of qualifying payments
- Holding eligible loan types (e.g., Direct Loans, Perkins Loans)
It's essential for borrowers to review the specific requirements of each program to determine their eligibility.
#### Application Process
The application process for loan forgiveness can vary depending on the program. Generally, borrowers must:
1. **Confirm Eligibility**: Review the criteria for the specific forgiveness program.
2. **Complete the Application**: Fill out the necessary forms, which may include employment certification forms for PSLF.
3. **Submit Documentation**: Provide any required documentation to verify employment and payment history.
4. **Follow Up**: Keep track of the application status and respond to any requests for additional information.
#### Conclusion
The **US Department of Education Loan Forgiveness** programs offer invaluable opportunities for borrowers to reduce their student loan debt. Understanding the various options, eligibility requirements, and application processes is essential for those seeking financial relief. By taking advantage of these programs, borrowers can potentially achieve significant savings and work towards a debt-free future. If you believe you may qualify, it’s advisable to gather your loan information, review your employment history, and consult with your loan servicer to explore your options.