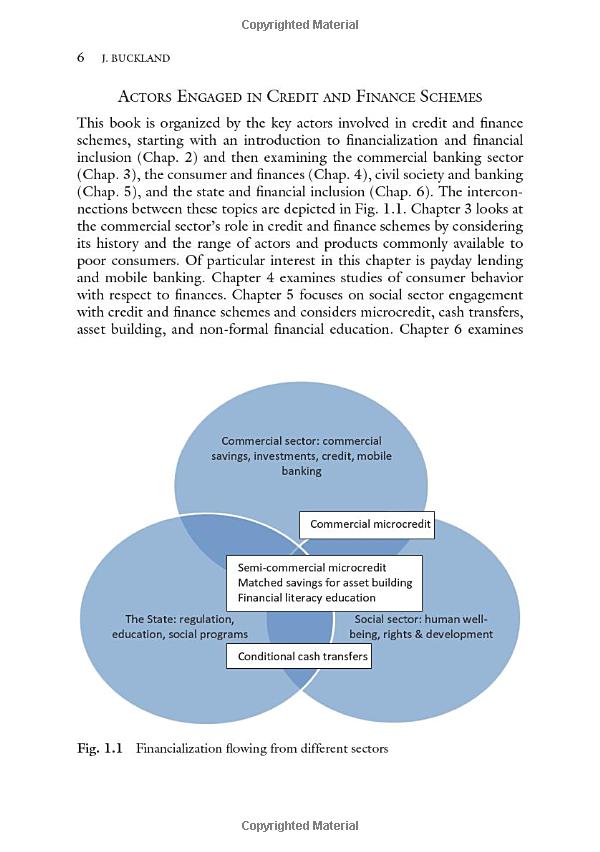
Understanding Loan Receivable: A Comprehensive Guide to Managing Your Financial Assets
#### What is Loan Receivable?Loan receivable refers to the amount of money that a lender expects to receive from a borrower as repayment for a loan. This fi……
#### What is Loan Receivable?
Loan receivable refers to the amount of money that a lender expects to receive from a borrower as repayment for a loan. This financial asset is crucial for lenders, as it represents future cash inflows and can significantly impact their financial health. Loan receivables can arise from various types of loans, including personal loans, mortgages, and business loans.
#### The Importance of Loan Receivable in Financial Management
For businesses and financial institutions, managing loan receivables is essential for maintaining liquidity and ensuring profitability. A well-managed loan receivable portfolio allows lenders to forecast cash flows accurately, assess credit risk, and make informed lending decisions. By understanding the dynamics of loan receivables, organizations can implement effective strategies to minimize defaults and optimize returns.
#### Types of Loan Receivables
There are several types of loan receivables, each serving different purposes and carrying varying levels of risk. Some common types include:
1. **Personal Loans**: These are unsecured loans given to individuals for personal use, such as consolidating debt or financing a large purchase.
2. **Mortgages**: Loans secured by real estate, where the property serves as collateral. Mortgage receivables are typically long-term and can be complex in nature.
3. **Business Loans**: Loans provided to businesses for operational needs, expansion, or equipment purchases. These can be secured or unsecured, depending on the lender's requirements.
#### How to Manage Loan Receivables Effectively
Effective management of loan receivables involves several key practices:

- **Regular Monitoring**: Keep track of outstanding loans, payment schedules, and borrower performance. This helps identify potential delinquencies early on.
- **Risk Assessment**: Conduct thorough credit assessments before approving loans to minimize the risk of defaults. This includes evaluating the borrower's credit history, income, and financial stability.
- **Collections Strategy**: Develop a clear strategy for collecting overdue payments. This may involve sending reminders, negotiating payment plans, or, in extreme cases, pursuing legal action.
- **Diversification**: Diversify your loan portfolio to spread risk across different types of borrowers and loan products. This can help mitigate the impact of defaults on your overall financial position.
#### Impact of Economic Conditions on Loan Receivables

Economic fluctuations can significantly affect loan receivables. During economic downturns, borrowers may struggle to meet their repayment obligations, leading to increased defaults and reduced cash inflows for lenders. Conversely, in a robust economy, borrowers are more likely to be financially stable, resulting in lower default rates and healthier loan receivable portfolios.
#### Conclusion
In summary, loan receivable is a vital component of financial management for lenders. By understanding its significance, types, and effective management strategies, organizations can optimize their loan portfolios and enhance their financial stability. As economic conditions change, staying vigilant and adaptable in managing loan receivables will be crucial for long-term success.